Mercedes-Benz M950F: Forskjell mellom revisjoner
(Ny side: Wankelmotor fra slutten av 60tallet. Totalt ble det bygget 12 motorer. {| class="wikitable float-right" ! colspan="2" style="text-align:center; color:#000; background:#9FB6CD;"| Daimle...) |
mIngen redigeringsforklaring |
||
| (7 mellomliggende revisjoner av samme bruker vises ikke) | |||
| Linje 1: | Linje 1: | ||
Wankelmotor fra slutten av 60tallet. | Wankelmotor fra slutten av 60tallet. | ||
{| class="wikitable float-right" | {| class="wikitable float-right" | ||
| Linje 6: | Linje 6: | ||
| colspan="2" class="center" | [[Bilde:DB_M950F.jpg|250px|]]<br>''Damler-Benz M950F'' | | colspan="2" class="center" | [[Bilde:DB_M950F.jpg|250px|]]<br>''Damler-Benz M950F'' | ||
|- | |- | ||
! colspan="2" style="text-align:center; color:#000; background:#B9D3EE;"| 1969 - | ! colspan="2" style="text-align:center; color:#000; background:#B9D3EE;"| 1969 - 1970 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| colspan="2" style="text-align:center; color:#000; background:# | | colspan="2" style="text-align:center; color:#000; background:#E00000;"| '''Bensin''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'''Motor'''|| | |'''Motor'''|| M950F | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'''Variant'''|| Wankel | |'''Variant'''|| Wankel | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'''Vekt tørr'''|| | |'''Vekt tørr'''|| Kg | ||
|- | |- | ||
| '''Byggeår'''|| 1969 - | | '''Byggeår'''|| 1969 - 1970 | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'''Ytelse'''|| 350 Hk @ 7000 o/min | |'''Ytelse'''|| 350 Hk @ 7000 o/min | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'''Dreiemoment'''|| | |'''Dreiemoment'''|| Nm @ o/min | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'''Innsprøytning'''|| | |'''Innsprøytning'''|| | ||
| Linje 55: | Linje 55: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
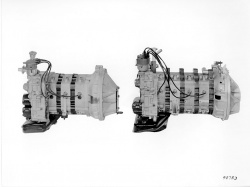
Mercedes-Benz M 950 er en prototype Wankel-motor. Den ble først beskrevet i Wolf-Dieter Bensingers essay "Der heutige Entwicklungsstand des Wankelmotors" fra 1969, publisert i januar 1970. | |||
Motoren ble utviklet av Daimler-Benz sin Wankel-motoravdeling, ledet av Bensinger. Rundt 100 enheter ble bygget, hvorav noen 3- og 4-rotorenheter ble installert i Mercedes-Benz C 111 eksperimentelle sportsbil, fra 1969 til 1970, som en midtmotor. | |||
Selv om M 950 var planlagt for kommersiell introduksjon i 1970 som en 2-rotormotor, hadde ikke M 950 nådd serieproduksjonsstadiet i 1972. | |||
Daimler-Benz utviklet deretter en etterfølger til M 950, M 951, men Daimler-Benz sin Wankel-motorutvikling ble forlatt i 1976. | |||
Engine type M 950 F | |||
Number of cylinders / arrangement three-rotor Wankel engine | |||
Total displacement chamber volume 3 x 600 cc | |||
Compression ratio 9.3 | |||
Rated output 280 hp / 206 kW at 7000 rpm | |||
Rated torque 294Nm at 4000 - 5500 rpm | |||
Fuel system direct injection, mechanically controlled; Bosch 3-plunger injection pump | |||
Cooling water cooling / pump; radiator in the car's front | |||
Lubrication pressure circulation lubrication | |||
Electric system 12 V | |||
Generator three-phase AC | |||
Starter electrical | |||
Ignition transistor ignition | |||
Fuel tank: position / capacity in the lateral frame side rails / 2 x 60 litre | |||
Fuel supply piston pump as part of the injection pump | |||
-- | |||
The extremely rare (12 total built) Mercedes-Benz M950F was a normally aspirated Wankel engine mounted in experimental Mercedes-Benz C111 vehicles, built in 1969-70. There were two versions: 3-rotor engine (600 cc each) with power output of 280 hp at 7000/min, and a later version 4-rotor engine (600 cc each) with power output of 350 hp at 7000/min. | |||
The experimental Mercedes-Benz C111 containing the (code named M950F) engine was shown to the public at the 1969 Frankfurt International Motor Show. | |||
This was a totally experimental car from Daimler-Benz, and they gave up on the rotary due mainly to poor fuel consumption. | |||
C 111 Specifications (First Version) | |||
Combustion principle Wankel | |||
Configuration in front of rear axle (mid engine) | |||
Engine type M 950 F | |||
Number of cylinders / arrangement three-rotor Wankel engine | |||
Total displacement chamber volume 3 x 600 cc | |||
Compression ratio 9.3 | |||
Rated output 280 hp / 206 kW at 7000 rpm | |||
Rated torque 294Nm at 4000 - 5500 rpm | |||
Fuel system direct injection, mechanically controlled; Bosch 3-plunger injection pump | |||
Cooling water cooling / pump; radiator in the car's front | |||
Lubrication pressure circulation lubrication | |||
Electric system 12 V | |||
Generator three-phase AC | |||
Starter electrical | |||
Ignition transistor ignition | |||
Fuel tank: position / capacity in the lateral frame side rails / 2 x 60 litre | |||
Fuel supply piston pump as part of the injection pump | |||
Gearing 5-speed manual transmission ZF 5 DS-25/1 | |||
Shifting central floor gear shift lever | |||
Clutch dry single-disc clutch | |||
Synchromesh gears I - V | |||
Final drive ratio 3.166 | |||
Maximum speed 260 km/h | |||
Acceleration 0-100 km/h 5 sec (2 occupants) | |||
C 111 Specifications (Second Version) | |||
Combustion principle Wankel | |||
Configuration in front of rear axle (mid engine) | |||
Engine type M 950 F | |||
Number of cylinders / arrangement four-rotor Wankel engine | |||
Total displacement chamber volume 4 x 600 cc | |||
Compression ratio 9.3 | |||
Rated output 350 hp / 257 kW at 7000 rpm | |||
Rated torque 392Nm at 4000 - 5500 rpm | |||
Fuel system direct injection, mechanically controlled; Bosch 4-plunger injection pump | |||
Cooling water cooling / pump; radiator in the car's front | |||
Lubrication pressure circulation lubrication | |||
Electric system 12 V | |||
Generator three-phase AC | |||
Starter electrical | |||
Ignition transistor ignition | |||
Fuel tank: position / capacity in the lateral frame side rails / 2 x 60 litre | |||
Fuel supply piston pump as part of the injection pump | |||
Gearing 5-speed manual transmission ZF 5 DS-25/1 | |||
Shifting central floor gear shift lever | |||
Clutch dry double-disc clutch | |||
Syncromesh gears I - V | |||
Final drive ratio 2.975 | |||
Maximum speed 300 km/h | |||
Acceleration 0-100 km/h 4.8 secs (2 occupants) | |||
==Technical specifications== | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|+Technical specifications | |||
|- | |||
! | |||
!3-rotor engine (M 950 F) | |||
!4-rotor engine (M 950/4) | |||
|- | |||
!Eccentricity <math>e</math> | |||
| colspan="2" style="text-align:center" |15 mm | |||
|- | |||
!Generating radius <math>R</math> | |||
| colspan="2" style="text-align:center" |99 mm | |||
|- | |||
!Equidistant <math>a</math> | |||
| colspan="2" style="text-align:center" |4 mm | |||
|- | |||
!Width <math>B</math> | |||
| colspan="2" style="text-align:center" |75 mm | |||
|- | |||
![[Wankel engine#Chamber volume|Chamber volume]] <math>V_k</math> | |||
| colspan="2" style="text-align:center" |{{#expr:3*3^0.5*15*75*(99+4)/1000 round-1}} cm<sup>3</sup> | |||
|- | |||
![[Wankel engine#Displacement|Displacement]] <math>V_h</math> | |||
| style="text-align:center" |{{#expr:2*3*3^0.5*15*75*(99+4)/1000*3 round-2}} cm<sup>3</sup> | |||
| style="text-align:center" |{{#expr:2*3*3^0.5*15*75*(99+4)/1000*4 round-2}} cm<sup>3</sup> | |||
|- | |||
![[Compression ratio|Compression]] <math>\varepsilon</math> | |||
| colspan="2" style="text-align:center" |9.3 | |||
|- | |||
![[Engine power|Rated power]] <math>P_e</math> | |||
| style="text-align:center" |205 kW | |||
| style="text-align:center" |260 kW | |||
|- | |||
![[Rotational frequency|Rated speed]] <math>n_e</math> | |||
| style="text-align:center" |7,000 min<sup>−1</sup> | |||
| style="text-align:center" | 6,000 min<sup>−1</sup> | |||
|- | |||
![[BMEP]] <math>p_e</math> | |||
| style="text-align:center" |1.05 MPa | |||
| style="text-align:center" |1.1 MPa | |||
|- | |||
! [[Mass]] <math>m</math> | |||
| style="text-align:center" |150 kg | |||
| style="text-align:center" |180 kg | |||
|- | |||
|Source | |||
| style="text-align:center" |<ref name="Bensinger 1973 p. 143">{{cite book | last=Bensinger | first=Wolf-Dieter | title=Rotationskolben-Verbrennungsmotoren | publication-place=Berlin, Heidelberg, New York | date=1973 | isbn=978-3-540-05886-1 | oclc=251737493 | language=de | page=143}}</ref> | |||
| style="text-align:center" |<ref name="Bensinger 1973 p. 143" /><ref name="Dobler 2000 pp. 441">{{cite journal | last=Dobler | first=Helmut | title=Renesis — ein neuer Wankelmotor von Mazda | journal=MTZ - Motortechnische Zeitschrift | publisher=Springer Science and Business Media LLC | volume=61 | issue=7-8 | year=2000 | issn=0024-8525 | doi=10.1007/bf03226583 | pages=441 | language=de}}</ref> | |||
|} | |||
;Power diagram of the M 950/4 | |||
{{Graph:Chart|width=300|height=200|type=line|xGrid=|yGrid=|xAxisTitle=Eccentric shaft speed (1/min)|y1AxisTitle=Power (kW)|legend=|y1Title=Power (kW)|x=1000,2000,3000,4000,5000,6000,7000,8000|y1=25,70,110,160,210,260,235,|interpolate=monotone}}<ref name="Bensinger 1973 p. 146">{{cite book | last=Bensinger | first=Wolf-Dieter | title=Rotationskolben-Verbrennungsmotoren | publication-place=Berlin, Heidelberg, New York | date=1973 | isbn=978-3-540-05886-1 | oclc=251737493 | language=de | page=146 fig. 164}}</ref> | |||
Nåværende revisjon fra 8. apr. 2023 kl. 14:14
Wankelmotor fra slutten av 60tallet.
Mercedes-Benz M 950 er en prototype Wankel-motor. Den ble først beskrevet i Wolf-Dieter Bensingers essay "Der heutige Entwicklungsstand des Wankelmotors" fra 1969, publisert i januar 1970.
Motoren ble utviklet av Daimler-Benz sin Wankel-motoravdeling, ledet av Bensinger. Rundt 100 enheter ble bygget, hvorav noen 3- og 4-rotorenheter ble installert i Mercedes-Benz C 111 eksperimentelle sportsbil, fra 1969 til 1970, som en midtmotor.
Selv om M 950 var planlagt for kommersiell introduksjon i 1970 som en 2-rotormotor, hadde ikke M 950 nådd serieproduksjonsstadiet i 1972.
Daimler-Benz utviklet deretter en etterfølger til M 950, M 951, men Daimler-Benz sin Wankel-motorutvikling ble forlatt i 1976.
Engine type M 950 F
Number of cylinders / arrangement three-rotor Wankel engine
Total displacement chamber volume 3 x 600 cc
Compression ratio 9.3
Rated output 280 hp / 206 kW at 7000 rpm
Rated torque 294Nm at 4000 - 5500 rpm
Fuel system direct injection, mechanically controlled; Bosch 3-plunger injection pump
Cooling water cooling / pump; radiator in the car's front
Lubrication pressure circulation lubrication
Electric system 12 V
Generator three-phase AC
Starter electrical
Ignition transistor ignition
Fuel tank: position / capacity in the lateral frame side rails / 2 x 60 litre
Fuel supply piston pump as part of the injection pump
--
The extremely rare (12 total built) Mercedes-Benz M950F was a normally aspirated Wankel engine mounted in experimental Mercedes-Benz C111 vehicles, built in 1969-70. There were two versions: 3-rotor engine (600 cc each) with power output of 280 hp at 7000/min, and a later version 4-rotor engine (600 cc each) with power output of 350 hp at 7000/min.
The experimental Mercedes-Benz C111 containing the (code named M950F) engine was shown to the public at the 1969 Frankfurt International Motor Show.
This was a totally experimental car from Daimler-Benz, and they gave up on the rotary due mainly to poor fuel consumption.
C 111 Specifications (First Version)
Combustion principle Wankel
Configuration in front of rear axle (mid engine)
Engine type M 950 F
Number of cylinders / arrangement three-rotor Wankel engine
Total displacement chamber volume 3 x 600 cc
Compression ratio 9.3
Rated output 280 hp / 206 kW at 7000 rpm
Rated torque 294Nm at 4000 - 5500 rpm
Fuel system direct injection, mechanically controlled; Bosch 3-plunger injection pump
Cooling water cooling / pump; radiator in the car's front
Lubrication pressure circulation lubrication
Electric system 12 V
Generator three-phase AC
Starter electrical
Ignition transistor ignition
Fuel tank: position / capacity in the lateral frame side rails / 2 x 60 litre
Fuel supply piston pump as part of the injection pump
Gearing 5-speed manual transmission ZF 5 DS-25/1
Shifting central floor gear shift lever
Clutch dry single-disc clutch
Synchromesh gears I - V
Final drive ratio 3.166
Maximum speed 260 km/h
Acceleration 0-100 km/h 5 sec (2 occupants)
C 111 Specifications (Second Version)
Combustion principle Wankel
Configuration in front of rear axle (mid engine)
Engine type M 950 F
Number of cylinders / arrangement four-rotor Wankel engine
Total displacement chamber volume 4 x 600 cc
Compression ratio 9.3
Rated output 350 hp / 257 kW at 7000 rpm
Rated torque 392Nm at 4000 - 5500 rpm
Fuel system direct injection, mechanically controlled; Bosch 4-plunger injection pump
Cooling water cooling / pump; radiator in the car's front
Lubrication pressure circulation lubrication
Electric system 12 V
Generator three-phase AC
Starter electrical
Ignition transistor ignition
Fuel tank: position / capacity in the lateral frame side rails / 2 x 60 litre
Fuel supply piston pump as part of the injection pump
Gearing 5-speed manual transmission ZF 5 DS-25/1
Shifting central floor gear shift lever
Clutch dry double-disc clutch
Syncromesh gears I - V
Final drive ratio 2.975
Maximum speed 300 km/h
Acceleration 0-100 km/h 4.8 secs (2 occupants)
Technical specifications
| 3-rotor engine (M 950 F) | 4-rotor engine (M 950/4) | |
|---|---|---|
| Eccentricity <math>e</math> | 15 mm | |
| Generating radius <math>R</math> | 99 mm | |
| Equidistant <math>a</math> | 4 mm | |
| Width <math>B</math> | 75 mm | |
| Chamber volume <math>V_k</math> | 600 cm3 | |
| Displacement <math>V_h</math> | 3600 cm3 | 4800 cm3 |
| Compression <math>\varepsilon</math> | 9.3 | |
| Rated power <math>P_e</math> | 205 kW | 260 kW |
| Rated speed <math>n_e</math> | 7,000 min−1 | 6,000 min−1 |
| BMEP <math>p_e</math> | 1.05 MPa | 1.1 MPa |
| Mass <math>m</math> | 150 kg | 180 kg |
| Source | [1] | [1][2] |
- Power diagram of the M 950/4